ESD Flooring for industrial workstations

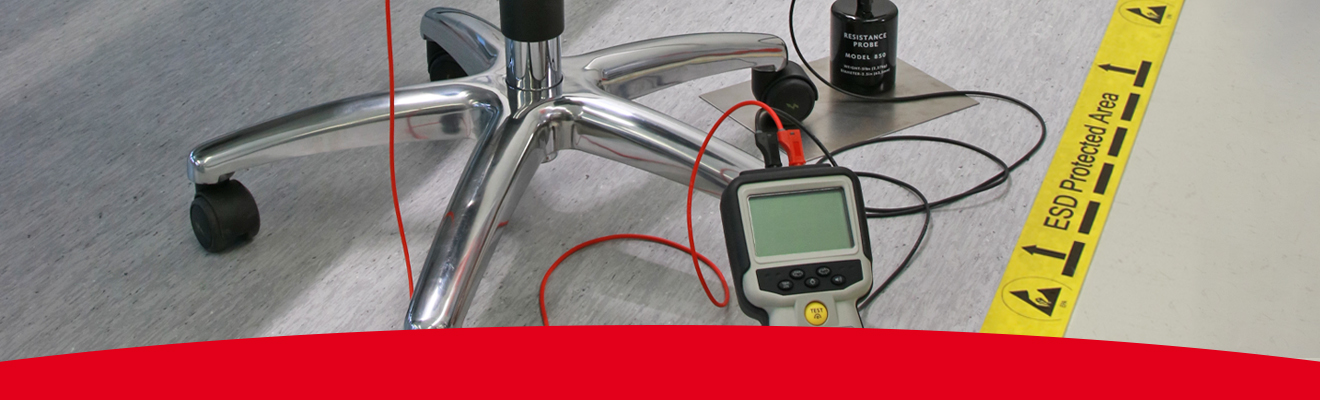
An ESD flooring is the key to the entire ESD protection system
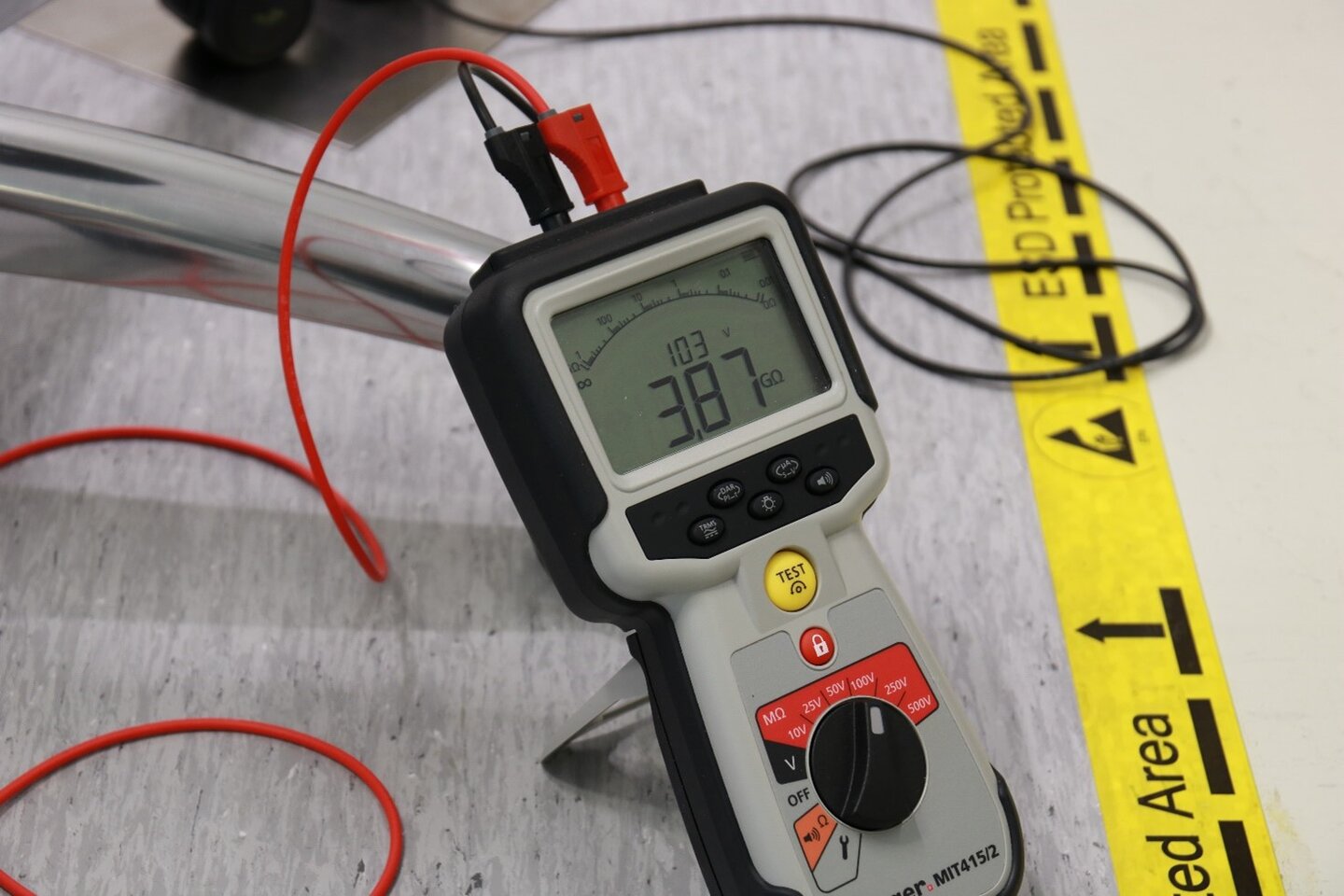
This is particularly important if you are using trolleys or ESD chairs. Based on the standard, it is not mandatory but really impacts ESD protection. An ESD mat or floor needs to be grounded in order for it to be ESD protected. Common point ground (CPG) is the way to connect all ESD grounding potentials together for ESD grounding and should be installed at the same time as the floor or mat.

ESD Floor mats
For small ESD protected areas, an ESD floor mat a few square meters in size is a good and simple choice. There are various types of mats with different features and materials. The choice of mats might be limited but it affects everything. Some mats work better with certain types of castors, shoes etc., although this cannot usually be ascertained before measuring ESD levels (i.e., surface conductivity) in a real environment.
Compliance information is sometimes available but as ‘everything affects everything’ some trial and error may be necessary. After the mat has been selected and assembled, it must be grounded and, depending on its size, one or more ground points are required.

"Cast" ESD floor
For new buildings, larger areas, or heavy loads it is smart to consider using a “cast” ESD floor. There are many different options for ESD flooring and choosing the right one might be difficult. We recommend that you consult ESD experts such as floor and ESD mat manufacturers and resellers for details, as well as the best options for your EPA.
Mark the ESD protected area
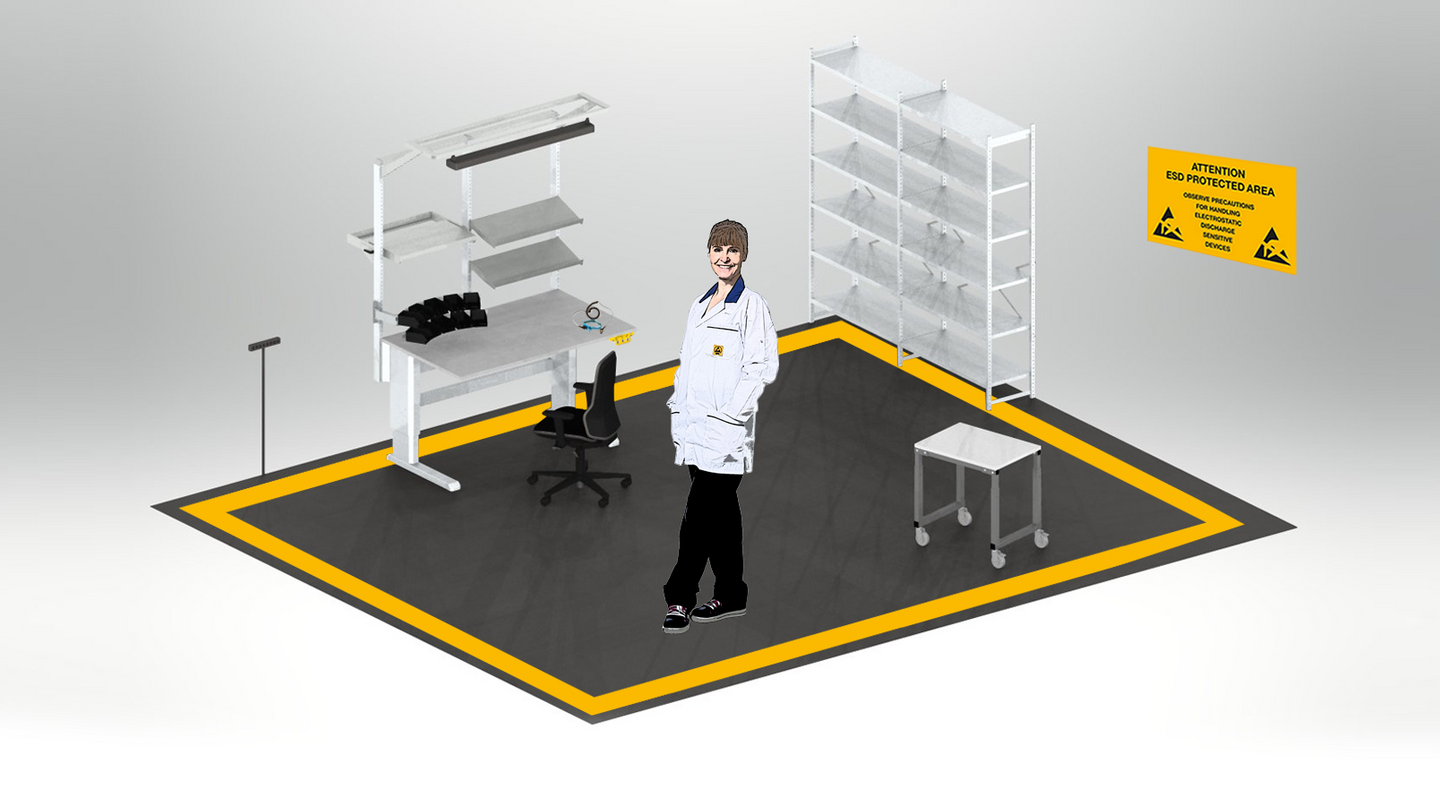
After being set up, an ESD-protected area should also be clearly marked. People entering an ESD area should be made aware that they must not accidentally pass the area without proper protection. For example, for a small area comprising a few square metres, it is a good idea to place yellow ESD stickers around the area to make it visible.
Want to learn more about ESD?

ESD related terms
|
ESD |
Electrostatic discharge. Occurs when two electrically charged objects come together and a charge is discharged. Could result in visible or hidden damage to an electrical component. |
|
EPA |
ESD-protected area |
|
ESDS |
Electrostatic discharge sensitive. A component that needs ESD protection. |
|
CONDUCTIVE MATERIAL |
Conductor = material that permits the flow of electrical current in one or more directions. Metals are often conductive, e.g., copper and aluminium. |
|
INSULATING MATERIAL |
Insulator = material that does not conduct electricity. The insulator can be electrostatically charged. Insulators can be plastic or wood, for example. |
|
STANDARDS |
IEC 61340-5-1: ESD standard widely used in Europe and ANSI S20.20 in the Americas. Both standards have a great number of similarities. |